Address: 493#, Xiazhaiwu village , Shiqiaotou town , Wenling city , Zhejiang province . China [email protected]
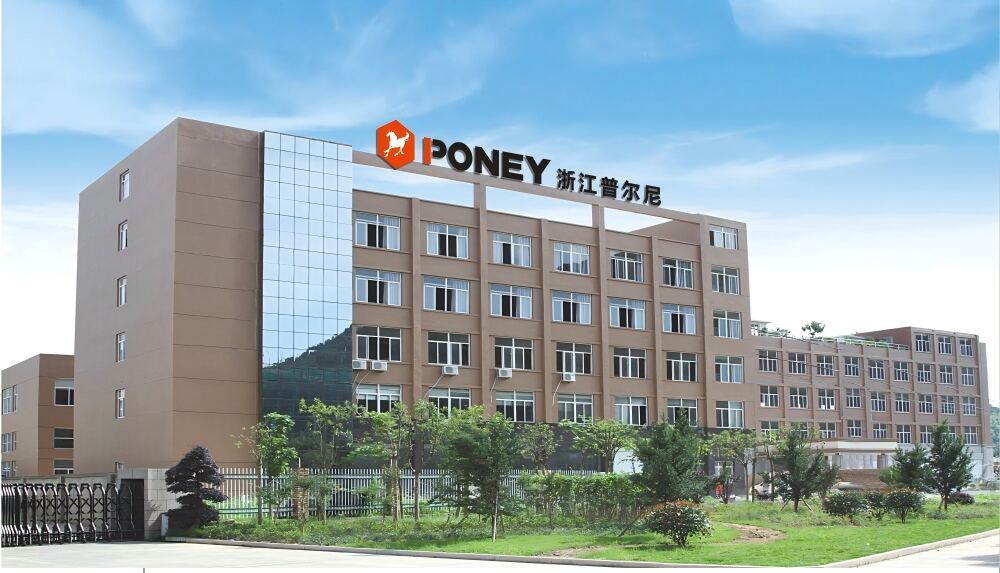

Located in Taizhou City, PONEY Limited has established itself as a pioneering manufacturer specializing in the production of welding machines, air plasma cutting machines, and car battery chargers. Our company is positioned a reliable partner by a vast range of products featuring ground - breaking technology, unique and modern designs. We are dedicated to offering efficient and effective solutions for our valued clients and helping create value.
Since its establishment in 2009, PONEY has developed a highly sophisticated system for manufacturing, R&D and after-sales services . We ensure superior quality, reliability, and safety by using state - of - the - art facilities, conducting rigorous in - line and final testing processes, and by implementing an integrated management system certified by BSCI and ISO9001.
Founding Year
Employees
Production Area
Monthly Production Capacity
Patents






We at PONEY are extremely proud of the following distinct advantages, ensuring our welding equipment and services stand out in the global market:

Unbeatable market prices, optimal value with guaranteed quality.
Adhere to top standards for reliable, high-performance products.

Premium welders (MIG/TIG/MMA), cutting equipment & car battery chargers for civil, light & heavy industries.

Efficient production & logistics ensure fast, on-time delivery.

Fully customized OEM solutions for designs, packaging & branding to meet your needs.

BSCI, ISO, CE, ETL, RoHS & Energy Efficiency Certified, compliant with global quality, environmental and safety standards.
 08 Jan 2026
08 Jan 2026
On January 8, 2026, the Technology Department of PONEY held a grand new product launch conference for welding machines in the multi-function conference hall on the second floor of the administrative building. Mr. Zhao Yuhao, Chairman of the company, ...
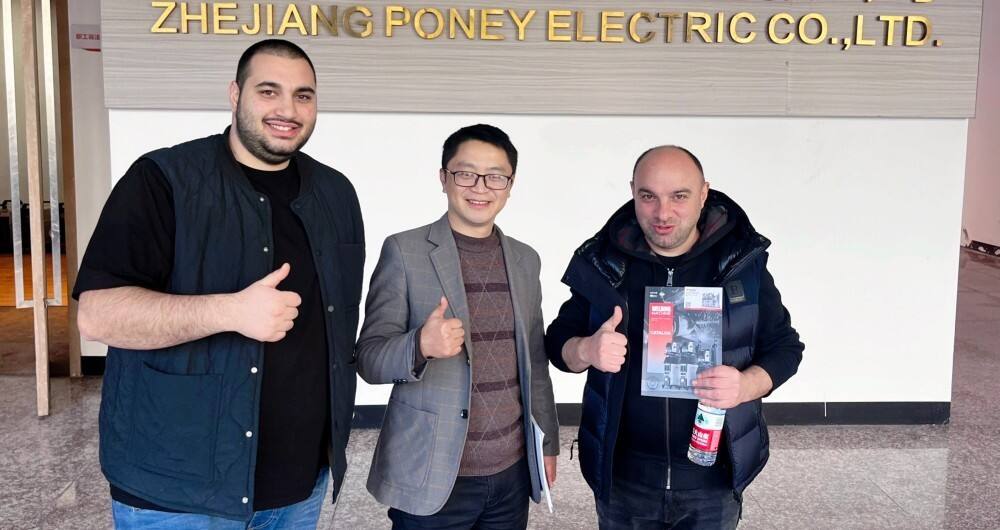 20 Dec 2025
20 Dec 2025
On December 20, 2025, PONEY warmly received a distinguished core procurement delegation from a renowned welding machine importer in Georgia, marking a significant step in expanding its global market presence. The visiting delegation was led by two pi...
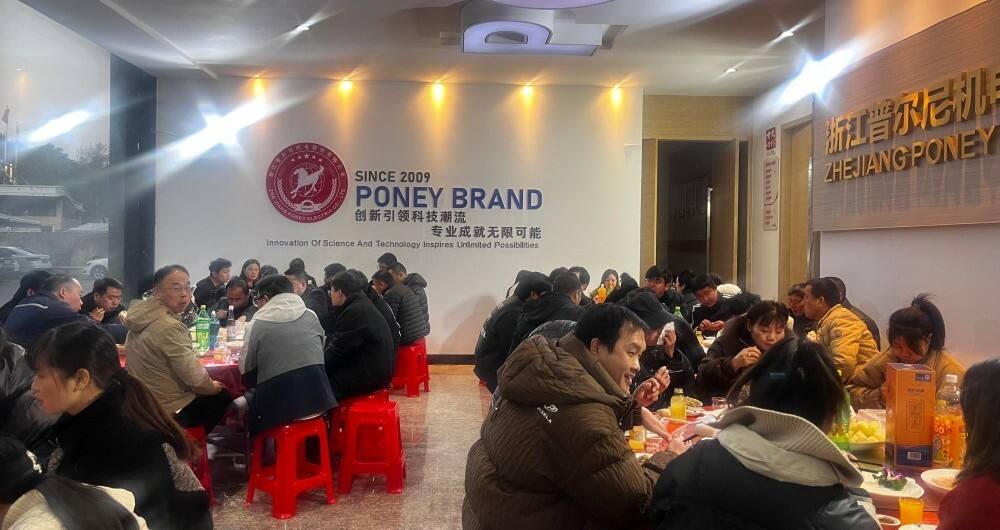 31 Dec 2025
31 Dec 2025
In-House Gala Unites Hearts for a New Journey December 31, 2025 On the evening of December 30, 2025, PONEY’s conference hall was transformed into a scene of radiant illumination and profound warmth, marking the commencement of the company&rsquo...